- AdFDJ03
-
C. Andrieu, N. de Freitas, A. Doucet, and M. Jordan, An
Introduction to MCMC for Machine Learning, Machine Learning
50 (2003), 5-43.
- AGR83
-
Adele Goldberg and Dave Robson, Smalltalk-80: the language, Addison
Wesley, 1983.
- ALSN01
-
Franz Achermann, Markus Limpe, Jean-Guy Schneider, and Oscar Nierstrasz,
Piccola - a Small Composition Language, Formal Methods for
Distributed Processing - a Survey of Object-Oriented Approaches
(Howard Bowman and John Derrick, eds.), Cambridge University
Press, 2001, pp. 403-426.
- AMST97
-
Gul Agha, Ian A. Mason, Scott F. Smith, and Carolyn L. Talcott, A
Foundation for Actor Computation, Journal of Functional Programming
7 (1997), no. 1, 1-72, Extensive formal explanation (72
pages) of Actor Systems. The `become' operator is one of the most difficult
to understand.
- BBC
-
Andrea Bracciali, Antonio Brogi, and Carlos Canal, Systematic component
adaptation, This paper introduces a CSP-like formalis to describe
the behavior of interface. The same notation is used to express adaptors and
once this is done it is possible to verify twhether the requirements are
matched within the adaptor.
- BBT01
-
Andrea Bracciali, Antonio Brogi, and Franco Turi, Coordinating
interaction patterns, Selected Areas in Cryptography, 2001, pp. 159-165.
- BFDV01
-
Werner Van Belle, Johan Fabry, Theo D'Hondt, and Karsten Verelst,
Experiences in Mobile Computing: The CBorg Mobile Multi-Agent
System, Proceedings TOOLSEE 2001, Zurich (http://borg.rave.org/) (Wolfgang
Pree, ed.), vol. 38, IEEE Computer Society Press, March 2001,
Summary of our experience with the self made Borg Mobile Multi
Agent System., pp. 1-9.
- BFF+95a
-
Eike Best, Hans Fleischack, Wojciech Fraczak, Richard P. Hopkins, Hanna
Klaudel, and Elisabeth Pelz, A Class of Composable High Level Petri
Nets with an Application to the Semantics of
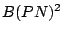 , Application
and Theory of Petri Nets (Giorgia De Michelis and Michel Diaz, eds.), Lecture
Notes in Computer Science, vol. 935, Springer Verlag, 1995,
Describes a set of high level operations to compose petri-nets.,
pp. 103-120.
, Application
and Theory of Petri Nets (Giorgia De Michelis and Michel Diaz, eds.), Lecture
Notes in Computer Science, vol. 935, Springer Verlag, 1995,
Describes a set of high level operations to compose petri-nets.,
pp. 103-120.
- BFF+95b
-
Eike Best, Hans Fleischhack, Wojciech Fraczak, Richard P. Hopkins, Hanna
Klaudel, and Elisabeth Pelz, An M-Net semantics of
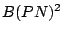 ,
STRICT (Jörg Dessel, ed.), Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Springer
Verlag, 1995, Describes the transformations necessary to compile
,
STRICT (Jörg Dessel, ed.), Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Springer
Verlag, 1995, Describes the transformations necessary to compile
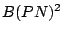 programs to High Level petri-nets, called M-Nets., pp. 85-100.
programs to High Level petri-nets, called M-Nets., pp. 85-100.
- BG98
-
Eike Best and Bernd Grahlmann, Format Descriptions, Tech. report,
Institut fur Informatik Marienburger Plaz 22 D-31141 Hildesheim, 1998,
Internal formats used by the PEP Tools.
- BH93
-
Eike Best and Richard P. Hopkins, B(PN) - a Basic Petri Net Programming
Notation, Proceedings PARLE'93 (A.Bode, M. Reeve, and G. Wolf, eds.),
Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 694, Springer Verlag, 1993,
A process algebra designed to map easily on petri nets.,
pp. 379-390.
- BK01
-
Meredith Beveridge and Philip Koopman, Jini meets embedded control
networking: a case study in portability failure.
- BL01
-
Joel Brinkley and Steve Lohr, U.S. v. Microsoft, McGraw-Hill, ISBN: 0
07 135588-X, 2001, Stunning facts how Microsoft crushes opponents
and how nobody seems to care.
- BMAPY97
-
Marius Bozga, Oded Maler, Amir Pnueli, and Sergio Yovine, Some
Progress in the Symbolic Verification of Timed Automata, Proc. 9th
International Conference on Computer Aided Verification (CAV'97)
(O. Grumberg, ed.), vol. 1254, Springer Verlag, 1997, Describes how
BDD (Binary Decission Diagrams) can be used in certain domains for a faster
timing verification of large Petri Nets., pp. 179-190.
- BOP
-
R. Bastide, O.Sy., and P. Palanque, Formal specification and prototyping
of corba systems, Proceedings of ECOOP'99, Spring Verlag LNCS 1628,
Uses Petri-nets to describe the behavior of CORBA objects.,
pp. 474-494.
- BP96
-
Eike Best and Ctuscia Palamidessi, Linear Constraint Systems as
High-Level Nets, CONCUR (Ugo Montanari and Vladimiro Sassone, eds.), vol.
1119, Springer Verlag, 1996, Makes the mapping from linear
programming to timed Petri-nets. Also proves that constructing a
reachability graph of timed Petri-Nets is NP-complete., pp. 498-513.
- Bra01
-
P. Brada, Towards Automated Component Compatibility Assessment,
Presented at Component Workshop ECOOP 2001, Budapest, Hungary (2001),
Stresses the importance of component compatibility guarantees.
However, implicit requirements are not addressed.
- Bro97
-
J. G. Brookshear, Computer science: An overview.
- CD99
-
Juan Carlos Cruz and Stéphane Ducasse, Coordinating Open Distributed
Systems, Proceedings Workshop on Future Trends of Distributed Computing
Systems, vol. 7, IEEE Computer Society Press, December 1999.
- CDGM97
-
A. Chavez, D. Dreilinger, R. Guttman, and P. Maes, A Real-Life
Experiment in Creating an Agent Marketplace, Proceedings of the
Second International Conference on the Practical Application of Intelligent
Agents and Multi-Agent Technology, London, UK, April 1997.
- CDK94
-
George Coulouris, Jean Dollimore, and Tim Kindberg, Distributed
Systems, Concepts and Design, Addison Wesley, 1994, Chapter
12 covers transactions, chapter 13 covers concurrency control and chapter 14
covers distributed transactions.
- CFKL91
-
Bryan Carpenter, Geoffrey Fox, Sung Hoon Ko, and Sang Lim, Object
Serialisation for Marshalling Data in a Java Interface to MPI,
Java Grande, 1991, Among other things shows benchmarking results
of Java Serialisation, pp. 66-71.
- CFL+99
-
R. Scott Cost, Tim Finin, Yannis Labrou, Xiaocheng Luan, Yun Peng, Ian Sobroff,
James Mayfield, and Akram Boughannam, An agent-based infrastructure for
enterprise integration, First International Symposium on Agent Systems and
Applications (ASA'99/Third International Symposium on Mobile Agents
(MA'99), 1999.
- CFP+01
-
C. Canal, L. Fuentes, E. Pimentel, J.M.Troya, and A. Vallecillo,
Extending CORBA Interfaces With Protocols, The Computer Journal
44 (2001), no. 5, 448-462, Argues that an extension to
IDL's might be appropriate.
- CG
-
Craig. M. Chase and Vijay K. Garg, Detection of Global Predicates:
Techniques and their Limitations, Tech. report, Parallel and Distributed
Systems Laboratory, Electrical and Computer Engineering Department, The
University of Texas.
- CL94
-
Robert Cyphner and Eric Leu, Repeatable and portable message-passing
programs, 22-31.
- CP95
-
Stephen Cranefield and Martin Purvis, Agent-based integration of
general-purpose tools, Proceedings of the CIKM'95 Workshop on Intelligent
Information Agents (Baltimore, Maryland) (Tim Finin and James Mayfield,
eds.), 1995.
- Cro96
-
J. Crowcroft, Open distributed systems, UCL Press, 1996.
- Dar59
-
Charles Darwin, On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural
Selection, or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle
for Life, 24 November 1859, The entire text of this historical
work can be found on
http://www.literature.org/authors/darwin-charles/the-origin-of-spieces/.
- DBS+01
-
K. Ducatel, M. Bogdanowicz, F. Scapolo, J. Leijten, and J.C. Burgelman,
Scenarios for Ambient Intelligence in 2010, IPTS-Sevile, see
http://www.cordis.lu/ist/istag.htm (2001), A set of nice written
scenarios wrt ambient intelligence.
- D'H95
-
Theo D'Hondt, Pico, http://pico.vub.ac.be/ (1995), Pico is an
educational language used at the VUB. This is the website.
- Dic00
-
C. Dichev, Advanced operating systems lecture notes.
- DK96
-
Dimitirs C. Dracopoulos and Simon Kent, Bulk Synchronous
Parallelisation of Genetic Programming, Applied Parallel Computing:
Industrial Strength Computation and Optimisation, Proceedings of the third
International Workshop PARA'96 (Berlin, Germany) (Jerzy Wasniewski,
ed.), Springer-Verlag, 1996, pp. 216-226.
- Edw99
-
W. Keith Edwards, Core JINI, ISBN: 0-13-014469-X, The Sun Microsystems
Press Java Series, Prentice Hall PTR, Upper Saddle Rive, NJ 07458, 1999,
Explains the reasons behind and the implementation of Jini.
- EK98
-
Mohammed Elkoutbi and Rudolf K. Keller, Modelling Interactive Systems
with Hierarchical Coloured Petri Nets, Proceedings of the Conference on
High Performance Computing (1998), Given a set of UML usage
scenarios, a Petri-net is generated.
- EN94
-
Javier Esparza and M. Nielsen, Decidability Issues for Petri Nets,
Bulletin of the EATCS, vol. 52, February 1994, A good
introduction to the decidability issues of Petri-nets, pp. 115-129.
- ERV96
-
Javier Esparza, Stefan Romer, and Walter Vogler, An Improvement of
McMillan's Unfolding Algorithm, Int'l Proceedings of Tools and
Algorithms for Construction and Analysis of Systems, Lecture Notes in
Computer Science, vol. 1055, Springer Verlag, 1996, Explains the
reason behind Petri-net unfolding, their limitations and improves McMillans
original algorithm., pp. 87-106.
- ES
-
Michael Erdmann and Rudi Studer, Ontologies as Conceptual Models for XML
Documents, Tech. report, Institut fur Angewandte Informatik und Formale
Beschreibungsverfahren (AIFB) University of Karlsruhe (TH) D-76128
Karlsruhe (Germany) {erdmann, studer}@aifb.uni-karlsruhe.de.
- FDF03
-
R. Figueiredo, P. Dinda, and J. Fortes, A case for grid computing on
virtual machines, Proceedings International Conference on Distributed
Computing Systems (ICDCS) (2003).
- FFMM94
-
T. Finin, R. Fritzson, D. McKay, and R. McEntire, KQML as an agent
communication language, Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on
Information and Knowledge Management (CIKM'94) (Gaithersburg, MD, USA)
(N. Adam, B. Bhargava, and Y. Yesha, eds.), ACM Press, 1994, pp. 456-463.
- FG98
-
Hans Fleischhack and Bernd Grahlmann, A Compositional Petri Net
Semantics for SDL, ICATPN (J.Desel and M. Silva, eds.), Lecture Notes
in Computer Science, vol. 1420, 1998, Describes how SDL can be
converted to M-Nets by means of composition of a number of basic building
blocks., pp. 144-164.
- FKK95
-
Bause Falko, Peter Kemper, and Pieter Kritzinger, Abstract Petri-Net
Notation, Petri Net Newsletter 49 (1995), 9-27,
Describes an abstract Petri-net notation which is suitable for TEX.
Otherwise quite unreadable and probably not suitable as a Petri-net syntax.
- Fla94
-
Peter Flach, Simply Logical, Intelligent Reasoning by Example, ISBN:
0-471-94152-2, Wiley Professional Computing, 1994, Interesting book
that explains how 'intelligent' programs can be written in prolog. Covers a
lot of examples and a lot of different approaches/techniques.
- G.01
-
Booch G., Object Oriented Analysis and Design with Applications,
Santa Clara, California: The Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Company, Inc.,
2001.
- Gar97
-
Vijay K. Garg, Observation and Control for Debugging Distributed
Computations, 3rd international workshop on Automated Debugging
(AADEBUG97) (Linköping, Sweden), 1997, pp. 1-12.
- GF93
-
Michael R. Genesereth and Richard E. Fikes, Knowledge interchange format
version 3.0 reference manual, Tech. report, Computer Science Department
Stanford University Stanford, California 94305, 1993.
- GK99
-
Günther Kniesel, Type-Safe Delegation for Run-Time
Component Adaption, Lecture Notes in Computer Science
1628 (1999), 351.
- Gol89
-
David E. Goldberg, Genetic Algorithms in Search, Optimisation and
Machine Learning, ISBN: 0-201-15767-5, 1989.
- Gra
-
Bernd Grahlmann, PEP: A Programming Environment based on
Petri nets, Institut fur Informatik Marienburger Plaz 22 D - 31141
Hildesheim.
- Gre65
-
Mendel Gregor, Versuche über Pflanzen-Hybriden, March 1865,
The entire text (also translated to English) of this historical work
can be found at http//www.mendelweb.org/.
- Gru93
-
Thomas R. Gruber, Towards Principles for the Design of Ontologies Used
for Knowledge Sharing, Formal Ontology in Conceptual Analysis and
Knowledge Representation (1993).
- GW93
-
V. Scott Gordon and Darrell Whitley, Serial and Parallel Genetic
Algorithms as Function Optimisers, Proceedings of the Fifth
International Conference on Genetic Algorithms (San Mateo, CA) (Stephanie
Forrest, ed.), Morgan Kaufman, 1993, pp. 177-183.
- HAAC+00
-
Harold Abelson, Don Allen, Daniel Coore, Chris Hanson, George Homsy,
Thomas F. Knight, Redhika Nagpal, Erik Rauch, Gerald J. Sussman, and Ron
Weiss, Amorphous Computing, Communications of the ACM 43
(2000), no. 5, 74-82.
- Har87
-
D. Harel, A Visual Formalism for Complex Systems, Science of
Computer Programming 8 3 (1987), 231-274.
- Hoa85
-
C.A.R. Hoare, Communicating Sequential Processes, International
Series in Computer Science, Prentice Hall, ISBN: 0 13 153271, 1985,
The reference on CSP.
- Hol
-
J.H Holland, Escaping Brittleness: The Possibilities of General
Purpose Learning Algorithms applied to Parallel Rule-Based
Systems, Machine Learning 2, 593-623.
- HWSS95
-
Thomas Haynes, Roger Wainwright, Sandip Sen, and Dale Schoenefeld,
Strongly Typed Genetic Programming in Evolving Cooperation
Strategies, Genetic Algorithms: Proceedings of the Sixth International
Conference (ICGA95) (Pittsburgh, PA, USA) (L. Eshelman, ed.), Morgan
Kaufman, 1995, pp. 271-278.
- JB99
-
Jan Bosch, Superimposition: A component Adaptation Technique,
Information and Software Technology 41 (1999), no. 5,
257-273.
- JCJO92
-
Ivar Jacobson, Magnus Christerson, Patrik Jonsson, and Gunnar Övergaard,
Object Oriented Software Engineering. A Use Case Driven
Approach, 1992.
- JDA97
-
Ellsberger J., Hogrefe D., and Saram A., SDL, Formal
Object-Oriented Language for Communicating Systems, London:
Prentice Hall, 1997.
- Jen94
-
K. Jensen, An Introduction to the Theoretical Aspects of Coloured
Petri Nets, A Decade of Concurrency (J.W. de Bakker, W.P. de Roever, and
G. Rozenberg, eds.), Lecture Notes In Computer Science, vol. 803, Springer
Verlag, 1994, Very good introduction to coloured petri nets. A
must read for everyone involved with petri-nets. Also covers formal
analysis of Petri Nets., pp. 230-272.
- JMW+91
-
Rumbaugh J., Blaha M., Premerlani W., Eddy F., and Lorensen W.,
Object-Oriented Modelling and Design, Prentice-Hall, 1991.
- Jør
-
Jens Bæk Jørgensen, Construction of Occurrence Graphs with
Permutation Symmetries Aided by the Backtrack Method, Tech. report,
Computer Science Department, University of Aarhus, Ny Munkegade, Bldg. 540,
DK-8000 Aarhus C, Denmark, Explains how to detect self-symmetries
during reachability analysis by means of backtracking. However, not a
published paper, it is a very interesting read.
- KCJ98
-
Lars M. Kristensen, Soren Christensen, and Kurt Jensen, The
Practitioner's Guide to Coloured Petri-nets, International Journal on
Software Tools for Technology Transfer (1998), 98-132, This paper
provides a comprehensive road map to the practical use of CPNets and the
Design/CPN tool. The paper is self-contained and does not assume any prior
knowledge of Petri nets.
- Kie96
-
T. Kielmann, Designing a Coordination Model for Open Systems, Proc.
1st International Conference on Coordination Models and Languages (Cesena,
Italy) (P. Ciancarini and C. Hankin, eds.), vol. 1061, Springer-Verlag,
Berlin, 1996, pp. 267-284.
- KLAPM96
-
Leslie Pack Kaelbling, Michael L. Littman, and Andrew P. Moore,
Reinforcement Learning: A Survey, Journal of Artificial
Intelligence Research 4 (1996), 237-285.
- Koz92
-
John R. Koza, Genetic programming; on the programming of computers by
means of natural selection, ISBN: 0-262-11170-5, The MIT Press, 1992.
- KRCE01
-
James Kennedy and with Yuhui Shi Russel C. Eberhart, Swarm
Intelligence, ISBN: 1-55860-595-9, Morgan Kaufman Publishers, 2001,
Covers a) philosophical aspects of evolutionary computing and b) the
algorithmic of co-evolving individuals.
- KV97
-
Ekkart Kindler and Tobias Vesper, A Temporal Logic for Events and
States in Petri Nets, Proceedings of the Workshop "Petri Nets in System
Engineering" (PNSE'97), Hamburg, September 1997, Describes a
non-sequential temporal logic for Petri-nets.
- Lak94
-
C. Lakos, Definition and Relationship to Coloured Nets, Tech. report,
Department of Computer Science, University of Tasmania, 1994.
- Lam77
-
Leslie Lamport, Time, clocks, and the ordering of events in a distributed
system., Communications of the ACM 21 (1977), no. 7, 558-656.
- Lea00
-
Doug Lea, Concurrent Programming in Java (2nd edition) Design Principles
and Patterns, ISBN: 0-201-31009-0, The Java Series, Addison Wesley, 2000,
The book on concurrent programming in Java. Covers a lot of
concurrency problems, discusses a lot of standard solutions. Does not cover
formal techniques and it seems like everything is reinvented with the start
of Java.
- LF93
-
L.Bull and T. Fogarty, Co-evolving Communicating Classifier Systems
for Tracking, Proc. Int'l Conference Neural Networks and Genetic
Algorithms (1993).
- LLPY97
-
K. Larsen, F. Larson, P. Pettersson, and W. Yi, Efficient Verification
of Real-Time Systems: Compact Data Structure and State-Space Reduction,
Presented at 18th IEEE Real-Time Systems Symposium. San Francisca,
California, USA, December 1997, Tries to solve the
memory-requirements of reachability checks of timed automata, pp. 14-24.
- LSMD96
-
Carine Lucas, Patrick Steyaert, Kim Mens, and Theo D'Hondt, Reuse
Contract: Managing the Evolution of Reusable Assets, ACM Press, October
1996, Describes how interface behaviour can be specified in an
abstract way, aiming at reuse of the described interface.
- Lyn96
-
Nancy A. Lynch, Distributed Algorithms, ISBN: 1-55860-348-4, Morgan
Kaufman, 1996.
- MA97
-
John O. Moody and Panos J. Antsaklis, Deadlock avoidance in petri-nets
with uncontrollable transitions, Tech. report, Technical Report of the ISIS
Group at the University of Notre Dame ISIS-97-016, October 1997.
- Mil99
-
Robin Milner, Communicating and Mobile Systems: the
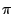 -calculus,
Cambridge University Press, May 1999, Extensive formal explanation
of the
-calculus,
Cambridge University Press, May 1999, Extensive formal explanation
of the 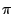 calculus. The concept `mobility through channelling' is quite
interesting.
calculus. The concept `mobility through channelling' is quite
interesting.
- Mon93
-
David J. Montana, Strongly Typed Genetic Programming, Tech. Report
#7866, 10 Moulton Street, Cambridge, MA 02138, USA, 7 1993.
- Moo96
-
Simon W. Moore, Data-flow machines, University of Cambridge,
http://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/users/swm11/dataflowlecture/dataflowlecture.html
#compare, 25 April 1996, Historically interesting pages. It is
surprising to see how the evolution of dataflow machines follows closely the
evolution of Petri nets.
- Mor96
-
L. Morgenstern, The Problem with Solutions to the Framing
Problem, The Robot's Dilemma Revisited: The Frame Problem in Artificial
Intelligence (K. M. Ford and Z. Pylyshyn, eds.), Ablex Publishing Co.,
Norwood, New Jersey, 1996.
- MSBW94
-
Arthur McCord Majority S. Blumenthal, Herbet S. Lin and Leslie M. Wade,
Academic Careers for Experimental Computer Scientists and
Engineers, ISBN:0-309-04931-8, Computer Science and Telecommunications
Board, 1994, Investigates how computer science contributions should
be measured.
- Mur89
-
T. Murata, Petri nets: Properties, analysis and applications, 1989.
- MW99
-
Ronaldo Menezes and Alan Wood, Distributed Garbage Collection of Tuple
Space in Open Linda Coordination System, Proc. of the 14th International
Syposium onComputer and Information Sciences (Kusadasi, Turkey), 1999,
pp. 957-965.
- Nas50a
-
J.F. Nash, The bargaining problem, Econometrica 18 (1950),
155-162.
- Nas50b
-
to3em, Equilibrium points in n-person games, Proceedgins of the
National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 36
(1950), 48-49.
- Nas51
-
to3em, Non-cooperative games, Annals of Mathematics 54
(1951), 286-295.
- Nas53
-
to3em, Two person cooperative games, Econometrica 21 (1953),
128-140, The historical papers that gave impulse to a whole new
field of research.
- NU97
-
Marian H. Nodine and Amy Unruh, Faciliating open communication in agent
systems: The infosleuth infrastructure, Agent Theories, Architectures, and
Languages, 1997, pp. 281-295.
- OFM97
-
A. Olsen, O. Fgremand, and B. MllerPedersen, System Engineering using
SDL-92, Norh Holland, 1997, A Book an SDL92 and how to use it in
a system engineering process.
- OHE96
-
Robert Orfari, Dan Harkey, and Jeri Edwards, The Essential
Distributed Objects Survival Guide, ISBN: 0-471-12993-3, John Willey
and Sons, 1996, A funny book, which covers CORBA as well as
COM/OLE.
- Ore98
-
Peyman Oreizy, Decentralized software evolution, Proceedings of the
International Conference on the Principles of Software Evolution (IWPSE1)
(1998).
- Pet62
-
C.A. Petri, Comunication by Means of Automata (Kommunikation mit
Automaten), The original Petri-nets paper.
- Pet81
-
James L. Peterson, Petri Net Theory and the Modeling of Systems,
Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey, April 1981, Chapter
7 describes how a number of extensions to Petri-nets break certain
decidability issues.
- PM93
-
P.Altenbernd and R. Milczewski, Description of Timing Problems Using
Petri Nets for Level-Independent Timing Verification, Int'l Proceeding
ACM/SIGDA Workshop on Timing Issues in the Specification and Synthesis of
Digital Systems (TAU) (1993), Describes a number of complementary
techniques to verify the dynamic and static aspects of timed petri nets.
- Pnu77
-
A. Pnueli, The temporal logic of Programs, 8th annual symposium on
the Foundations of Computer Science, IEEE Computer Society Press, November
1977, Introduces the idea of using temporal logic as the logic basis
for proving correctness properties of concurrent programs.
- PW94
-
Jing Peng and Ronald J. Williams, Incremental Multi-Step
Q-learning, International Conference on Machine Learning, 1994,
pp. 226-232.
- RB02
-
Michiel Ronsse and Koen De Bosschere, Non-Intrusive Detection of
Synchronisation Errors Using Execution Replay, vol. 9, Automated
Software Engineering, no. 1, Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1 2002,
pp. 95-121.
- Reu
-
Ralf. H. Reussner, An Enhanced Model for Component Interfaces to
Support Automatic and Dynamic Adaptation, Tech. report, Chair
Informatics for Engineering and Science, Universität Karlsruhe.
- SAG98
-
Richard S. Sutton and Andrew G.Barto, Reinforcement Learning: An
Introduction, MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, A Bradford Book, 1998,
A very good (formal) introduction to reinforcement learning.
Q-Learning, SARSA and TD-learning are explained.
- SB92
-
Nicol N. Schraudolph and Richard K. Belew, Dynamic Parameter Encoding
for Genetic Algorithms, Machine Learning 9 (1992), 9-21.
- Sch87
-
Craig G. Schaeffer, The ARGOT Strategy: Adaptive Representation
Genetic Optimiser Technique, Proceedings of the second international
conference on Genetic Algorithms and their Applications (John C.
Grefenstette, ed.), Cambridge, Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, July 1987,
pp. 50-58.
- SEE99
-
The SEESCOA Project Proposal,
http://www.cs.kuleuven.ac.be/cwis/research /distrinet/projects/SEESCOA,
October 1999, Home of the SEESCOA research project.
- Sel01
-
Bran Selic, The Unbearable Lightness of Distributed Systems: a
Survivors Guide, Keynote Speech at the Components for Mobile Computing
workshop, 38th International TOOLS Conference, Zürich, Switzerland
(2001), Explains why programming open distributed systems is very
difficult.
- SGP94
-
Bran Selic, G. Gullekson, and P.T.Ward, Real-Time Object Oriented
Modelling, John Wiley and Sons, Inc, 1994, The book about ROOM.
- SJ75
-
G. J. Sussman and G. L. Steele Jr., Scheme, an Interpreter for Extended
Lambda Calculus, The original paper that introduces Scheme. The
paper itself is written on a good old fashioned typewriter, and some nostalgy
can be found between the lines. A must read.
- SKML
-
Luc Steels, F. Kaplan, A. McIntyre, and Joris Van Looveren, Crucial
Factors in the Origins of Word-meaning, Tech. report, Sony Computer Science
Laboratory - Paris, VUB Artificial Intelligence Laboratory - Brussels.
- Smi
-
S. F. Smith, A Learning System Based on Genetic Adaptive
Algorithms, Doctoral thesis, Department of Computer Science,
University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh 1980.
- SS89
-
Dale Schuurmans and Jonathan Schaeffer, Representational Difficulties
with Classifier Systems, Proceedings of the Third International
Conference on Genetic Algorithms (San Mateo, CA) (James D. Schaffer,
ed.), Morgan Kaufman, 1989, pp. 328-333.
- Sug98
-
Y. Sugiyama, Runtime software evolution based on version management,
1998.
- Sut88
-
Richard S. Sutton, Learning to Predict by the Methods of Temporal
Differences, Machine Learning 3 (1988), 9-44.
- Tes92
-
Gerald Tesauro, Practical Issues in Temporal Difference
Learning, Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 4,
Morgan Kaufman Publishers, Inc., 1992, pp. 259-266.
- TM87
-
Tommaso Toffoli and Norman Margolus, Cellular Automata Machines, a
New Environment for Modelling, The MIT Press, Cambridge Massachusetts,
1987.
- VHT00
-
A. Vallecillo, J. Hernandez, and J. Troya, Component interoperability,
Tech. Report ITI-2000-37, Departemento de Lenguajes y Ciencias de la
Computacion, University of Malaga, July 2000, Available at
http://www.lcc.uma.ex/ãv/Publicaciones/00/Interoperability.pdf. This paper
gives a good overview of the problems involved withou component/object
interoperability. It starts with basic syntactical conflicts and end with
semantic interoperability.
- Vre95
-
Gerard A.W. Vreeswijk, Formalising Nomic: Working on a Theory of
Communication with Modifiable Rules of Procedure, Tech. report,
Technical Report CS 95-02, Department of Computer Science, University of
Limburg, Maastricht, The Netherlands, 1995.
- WMC01
-
Bernhard Westfechtel, Bjorn P. Munch, and Reidar Conradi, A layered
architecture for uniform version management, IEEE Transactions on Software
Engineering 27 (2001), no. 12, 1111-1133.
- Wyd01
-
Bart Wydaeghe, PacoSuite: Component Composition Based on
Composition Patterns and Usage Scenarios, Ph.D. thesis, Vrije
Universiteit Brussel (VUB), November 2001.
Werner
2004-03-07