| Home | Papers | Reports | Projects | Code Fragments | Dissertations | Presentations | Posters | Proposals | Lectures given | Course notes |
|
|
Component Oriented Design of the SEESCOA Common Test Case: The Controller and Zoom BehaviourWerner Van Belle1* - werner@yellowcouch.org, werner.van.belle@gmail.com Abstract : This document describes the design of two components in the seescoa component system: the controller (or directory service, responsible for interconnecting most components) and the zoom behavior, responsible for providing linkage between the behaviour of two or more cameras.
Keywords:
camera zoom synchronized behavior distributed agreement coordination seescoa |
Contents
- Introduction
- component
Controller
- component
ZoomBehaviour
- About this document ...
Introduction
This document describes the design of two components. The Controller component and the CameraZoomBehaviour component. The first component takes care of setting up interconnections between components, and the second takes care of zooming cameras and coupling the zoom behaviour of a number of cameras. All components are part of a test case for the SEESCOA project.
component Controller
Description
The controller his functionalities are described as follows:
- If new components connect or reconnect, all interested components will be notified.
- If components die or disconnect, the interested components will be notified.
- The controller takes care of distribution errors.
- The controller takes care of booting the system
- When new component systems connect to the component infrastructure, the controller will upload the necesarry components to the target.
- The controller does not handle runtime events and does not synchronise between components, nor does it contain any application logics.
- The controller is not responsible for security, account management, nor choosing between different events.
- Offer component migration
- Remote update of components
Use Cases
Boot up
The boot up of the camera system contains two phases. The first phase covers the startup of the master-server, which also boots the controller. In the second phase, all cameras are looked up and new component systems can connect.
Phase 1: Master Component System Boot up
- [MCS]starts up with on the command line as only argument the controller component
- [MCS]loads the controller component
- [C]reads the initialisation file which contains a list of components to load
- [C]sends a create message to the MCS for all listed components
- [MCS]loads all components and initialises them. Normally, these component will not make connections with other components.
- [C]reads from the initialisation phase which components should connect to whom.
- [C]sends 'faked' Connect messages to all those components.
Phase 2: Client boot up
- [CCS]starts up with only the IP-address of the Master Component System on the command line.
- [CCS]connects to the MCS on the given address. Also connects to the Master Component System component.
- [MCS]accepts the connection, sends out a connect message to all interested parties (In this case, the controller)
- [C]looks up which components should exists at the given address.
- [C]sends out creation messages to the CCS for theses components
- [CCS]creates the components (loads the classes from the server)
- [C]after creation of the new components, the controller will send the correct 'faked' connect messages.
Component Join & Disjoin
Components can subscribe themselves to retrieve notification of certain new components within the system. For example, a user interface component would like to subscribe to new cameras. The user interface component will receive from the controller a connect message when a new camera joins (or is created).
Disconnecting component can be initiated from anywhere. Every delete command must be send to the controller, which will ask all components to disconnect themselves. If they don't the controller will take action. We will now illustrate connecting and disconnecting
Connecting
- [UI]is loaded and requests the controller a join for 'cameras'
- [CC]The camera component is loaded (by the controller)
- [C]Sends a HasJoined message to the UI
- [UI]Sends a connect message to the camera
Disconnecting
- [UI]wants to disjoin, sends a message to the controller
- [C]sends a disconnect to the UI
- [UI]disconnects all its ports
Unwanted Component Disconnection & Component System Disconnection
At the moment a component disconnects because there was an error (crash in the component) or a network failure, all dependent components will be notified with a HasDisjoined message. The messages which trigger such an action are
- ComponentSystemDisconnect
- ComponentSystemFailed
- ComponentFail
- ComponentDisconnected
Interfaces
port Component (noi=1)
- [in Init()]is send by the component system. This is guaranteed the first message a component will receive
- [in Connect(Port:<String>, With:<String>)]connects the sender his port With with the port Port of the receiver.
- [in Disconnect(Who:<String>, From:<String>)]disconnect Who from port From at receiver side
port ComponentSystem (noi=1)
- [in ComponentSystemDisconnect(ComponentSystem)]see description of the ComponentSystem component
- [in ComponentSystemFailed(ComponentSystem)]see description of the ComponentSystem component
- [in ComponentSystemConnect(ComponentSystem)]see description of the ComponentSystem component
- [in ComponentSystemQueueOverflow(ComponentSystem, Reason)]see description of the ComponentSystem component
- [in ComponentDisconnect(Component)]see description of the ComponentSystem component
- [in ComponentConnect(Component)]see description of the ComponentSystem component
- [in ComponentFailed(Component)]see description of the ComponentSystem component
- [out CreateComponent(BluePrint,]Name) is used to create all the necesarry components
multiport Controller (noi=1)
- [in LookingFor(NameSubstring)]Requests the controller to look for components with a name which contains the substring Name. In response to this message, the controller will send back all existing components and will from then on notify the requester of new components mathcing the given name.
- [out HasJoined(Who)]is send to notify everybody that Who has joined. This message is only send to all people subscribed to the given NameSubstring.
- [out HasDisjoined(Who)]is send as a notification of a disjoin. Is send only to subscribes components.
- [out Alife(Who)]is send out to check whether other component systems are still alive.
- [in AreYouAlife()]response of previous message
Message Traces
Camera Component System Boot Up
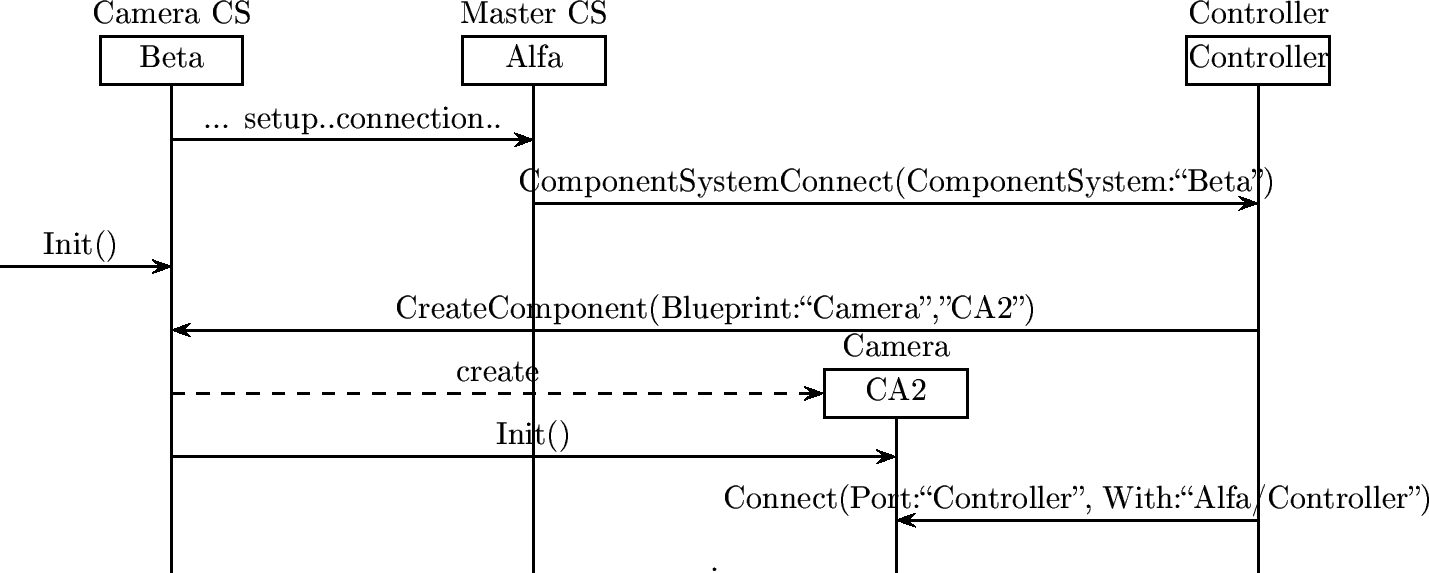
Master Component System Boot Up
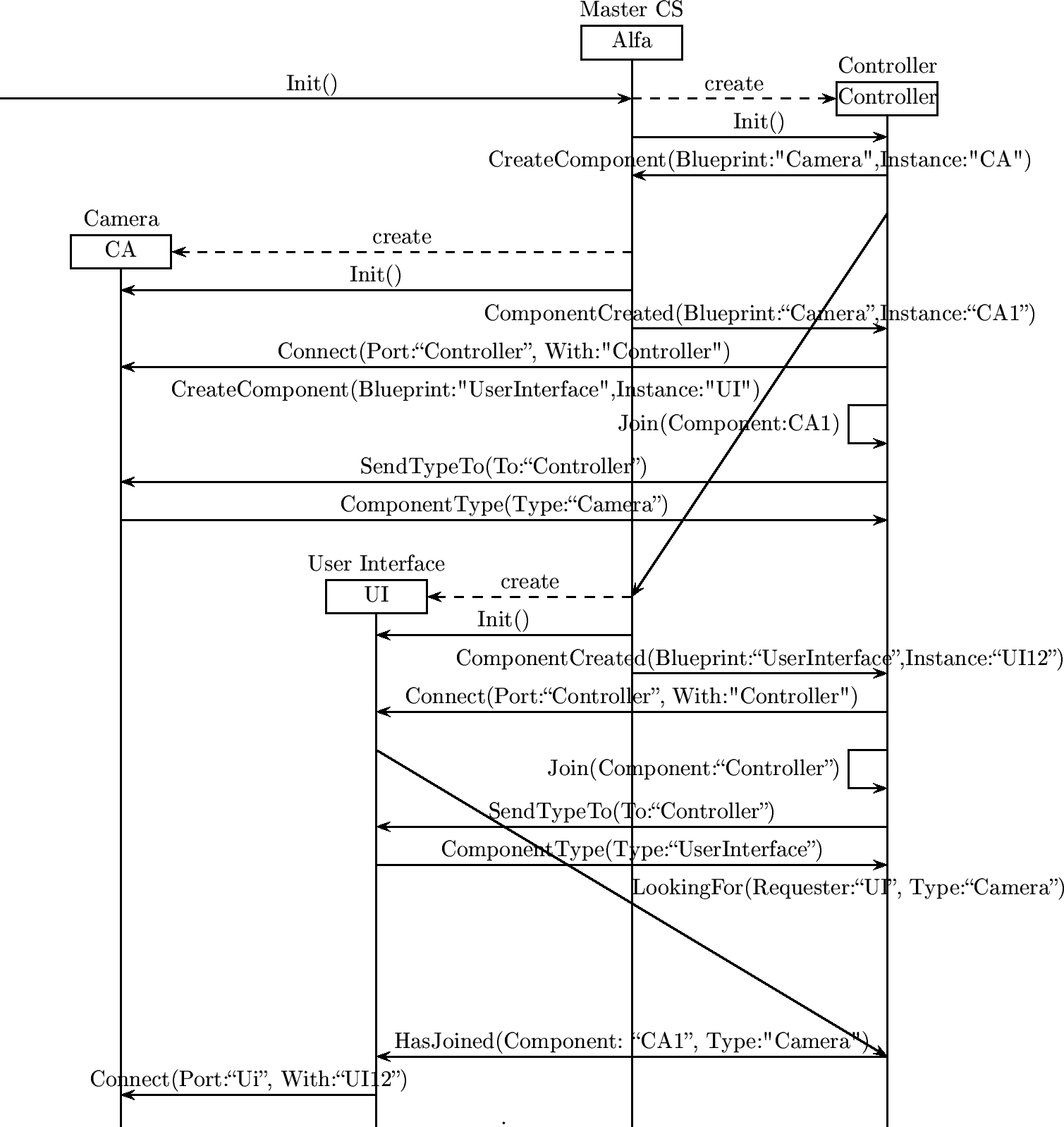
component ZoomBehaviour
Description
This is one of the plug in components, which is added to the system to show its flexibility.
- The zoom behaviour component is able to notify all subscribed components of a zoom changed notification.
- Zoom behaviour components can be coupled such that one camera zooms in while another zooms out and vice versa.
Use Cases
Logging of zoom-events
It is possible to log zoom events. If we want this we should connect to the zoom behaviour zoom changed port.
Selection of zoom events
It should be possible to select (prioritise) between a number of camera zoom events. If for example, 2 users are zooming in at the same time, together with an operator on the camera, the zoom behaviour controller should select one suer and stick to him during a certain period of activity.
Coupling of Zoom Behaviours
It should be possible to couple two (or more) cameras, such that the first camera zooms in while the second one zooms out. The constraints placed upon the zoom will be simple linear equations.
Interfaces
port Component (noi=1)
- [in Init()]is send by the component system. This is guaranteed the first message a component will receive
- [in Connect(Port:<String>, With:<String>)]See ComponentSystem component
- [in Disconnect(Who:<String>, From:<String>)]See ComponentSystem component
port Camera (noi<=1)
We will use a port to the camera status to obtain information about the maximum zooming parameters. This port is temporary. After obtaining the values this port is not used anymore.
- [out GetMax(Type:<String>)]requests the maximum zoom
- [out GetMin(Type:<String>)]requests the minimum zoom
- [in Value(Type:<String>, Value:<Integer>)]answers to both questions above
port ZoomRequest (noi=1)
This is the port offered by all cameras, which we have to implement in order to intercept certain zoom events.
- [in ZoomChangeRequest(From:<String>, Value:<Integer>)]incoming message from the camera, to ask whether the zoom can be changed to the given value. If this is allowed this component will send back a ZoomChangeAction.
- [out ZoomChangeAction(NewValue:<Integer>)]this message is send back to the camera when the zoom should actually change.
multiport ZoomChange (noi=1)
This port is necessary for anybody interested in zoom-change events. This is a stripped down interface of the camera-settings port and will be used by other ZoomBehaviour components.
- [out ZoomChanged(Camera:<String>, Value:<Integer> ,>InitiatedFrom<:[])]send out whenever the camera reports a change of value of the zoom. Camera is the name of the controlling camera. InitiatedFrom is an array with cameras, which has already send out a ZoomChanged.
port ZoomEvent (noi>=0)
This port is necessary for anybody who wants to report a ZoomChanged event at this controller.
- [in ZoomChanged(Camera:<String>, Value:<Integer>, >InitiatedFrom<:[])]Camera is the name of the camera for which the zoom has changed to value Value. In response to this message, this camera can change its own zoom factor. InitiatedFrom is an array of names which already sent a ZoomChanged.
port Behaviour (0<=noi<=1)
This port is used to change the formule used in each controller to react to ZoomChanged events.
- [in SetFormule(A:<Integer>[], B:<Integer>)]The formule is a linear equation. The integer array contains the coefficients. The integer B contains the extra value added to all this.
port UiDescription (0<=noi<=1)
This port can be used by anybody to receive an XML description of the behaviour port.
- [in GetUiDescription()]received from somewhere. In response we have to send back an XML tree which contains the possible behaviour of this component.
- [out PutUiDescription(Xml:<String>)]Send out. Will probably contain the parameters of the linear equation.
Example Message Sequences
Logging of Zoom events
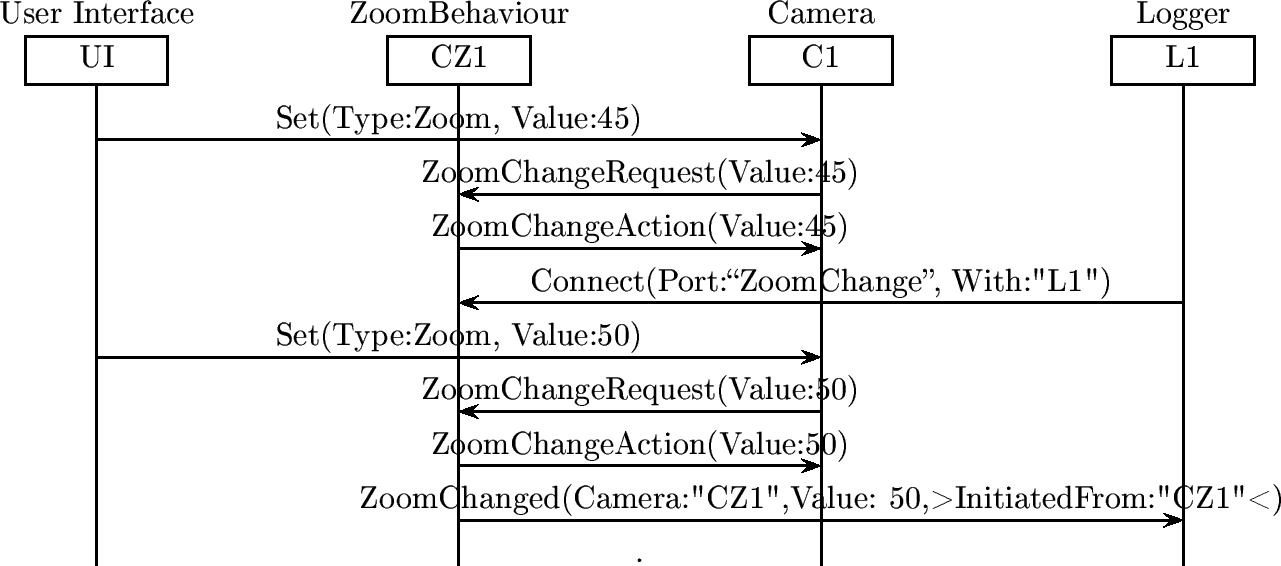
Coupling of 2 cameras
This is an example of two cameras coupled together.
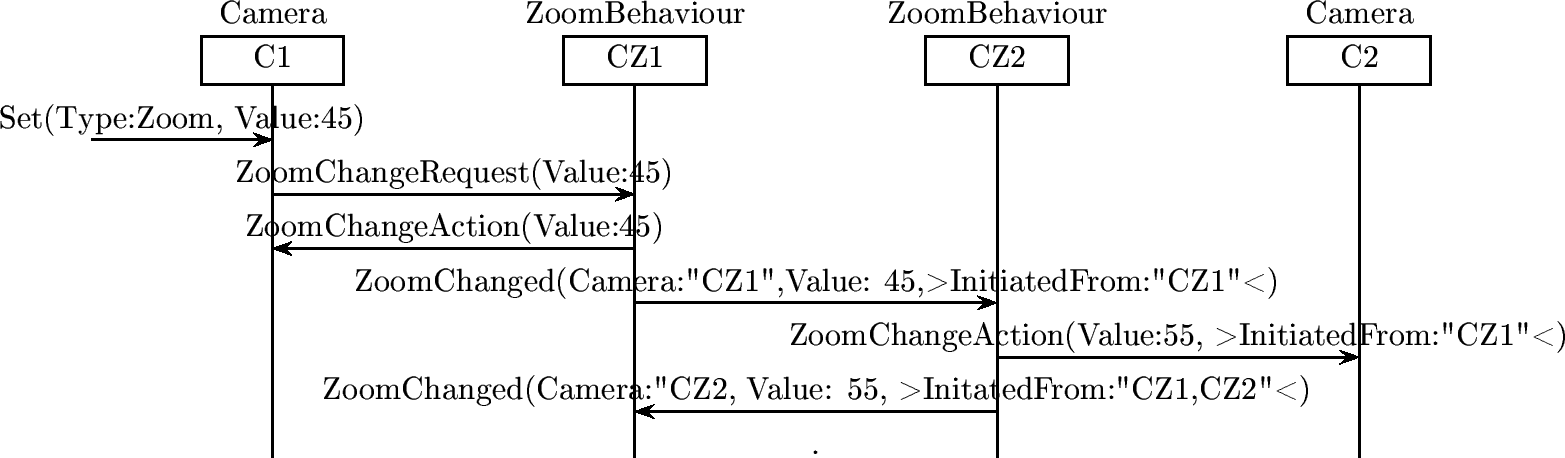
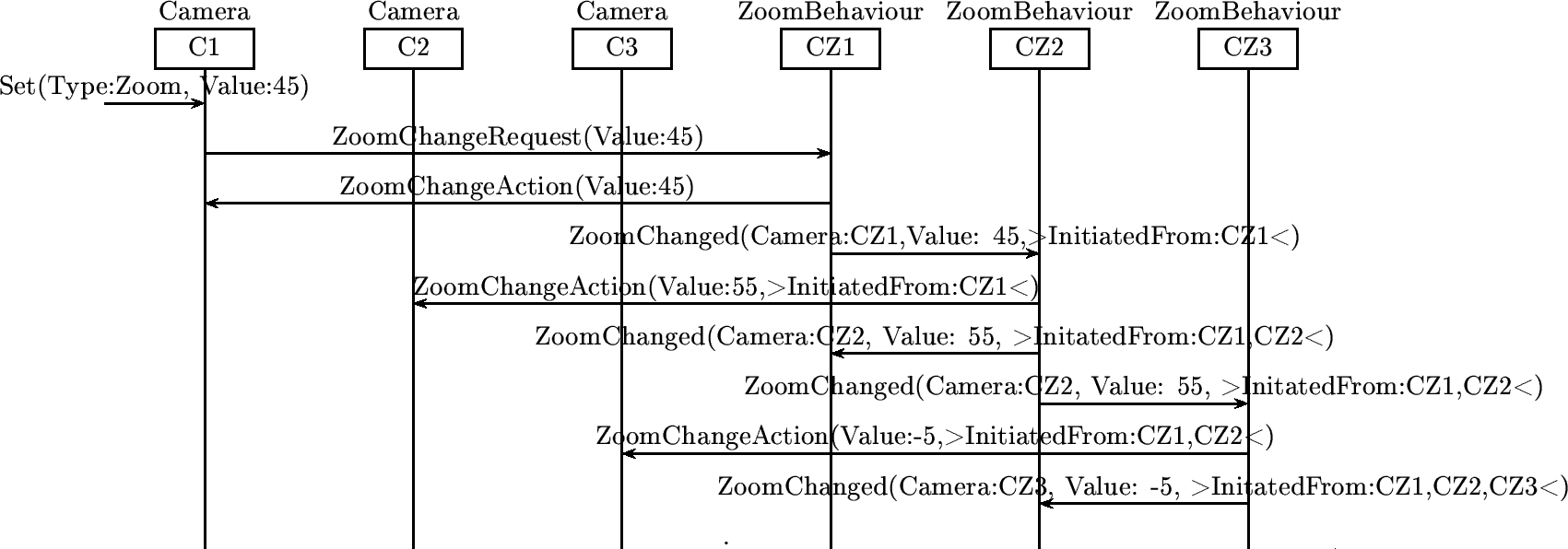
Coupling of 3 cameras, A with B, B with C
Below is an example of 3 cameras coupled together. The first is coupled to the second, the second is coupled to the third. The third camera is not immediately connected with the first.
| http://werner.yellowcouch.org/ werner@yellowcouch.org |  |