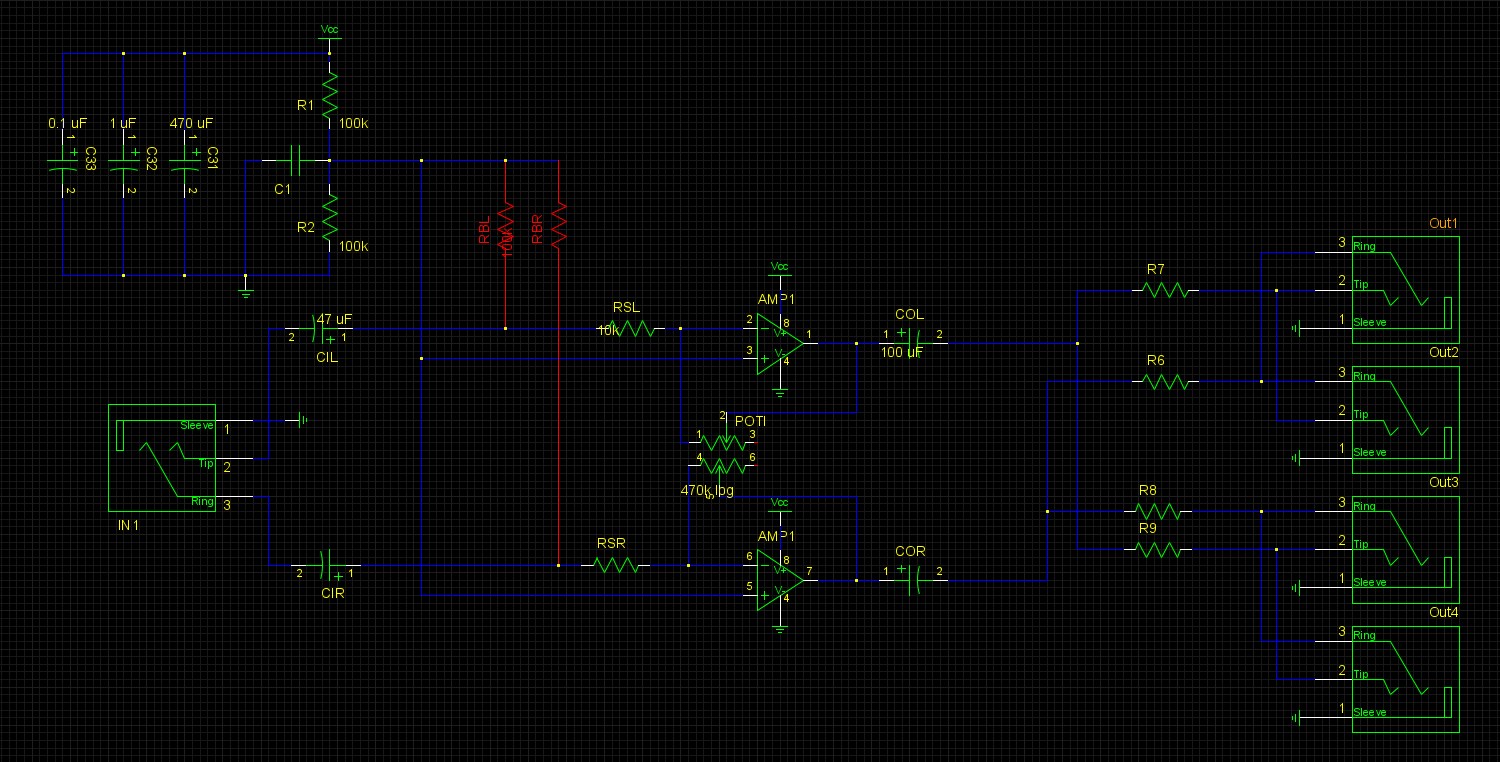
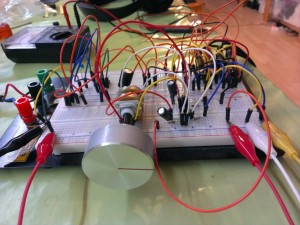
The old VCC/2 line, which I originally made with a second opamp has been replaced with a 100K resistor pair. Not the best solution because now it hums even louder. The grounds and the opamp bias have been properly decoupled this time (still hum). Some of the capacitor values have been lower in cutoff frequency (still hum). I tried placing a resistor over the input to remove the hum. That works if the resistor is ~680 Ohm. Yet in that case, if there is an input signal, it is barely amplified (no hum, no signal). Putting the entire thing in a metal box did not do a thing. So no pickup of magenetic fields (still hum). Replacing the powersupply with a batterypack resulted in >huray< no hum ! So it is most certainly a power supply problem. Hum removal is a non trivial problem. Grmpf.
Category Archives: Research & Development
Prototyping the Audio-splitter
Potental Backcovers as written by Scientific Reviewers
You probably know how back cover texts on books are always positive. No surprise there: they are written and/or selected by the publishers themselves, and they want to sell the book. Recently though, I wondered how they would read if scientific reviewers got their hand on the back-cover ?
Given my own experience with this breed of vultures, I believe the opinions will be wide-ranged, but will in general be self-involved and with an absolute disregard for the actual content. This is what I came up with:
1. This author paid us a lot, so it must be a good book.
2. This is really a boring book. We didn’t not get past the first chapter. Not even on the toilet. Probably it is good though. Good luck with this read !
3. We at Oxford/Stanford publishing recognize the excellent sales this book will offer to our partners.
4. This book has great potential.
5. We tried to read the book backward and couldn’t follow it. It’s probably scientific.
6. We didn’t like the font of the book.
7. There were no nice pictures in the book.
8. Why couldn’t the author give a dense outline of the book before starting with that lengthy introduction ?
9. As a professional editor and a high selling author of two and a half book, I believe our own work is so much more interesting than what you are holding in your hands right now. For instance, we ‘develop’ our characters in our manuscripts and we ‘work’ with the reader to achieve a greater understanding of the book’s emotional plot.
10. I had to read it and was not really interested. I finished the 540 pages in 3 hours and am not impressed.
11. I only read the first sentence of each page and the story still made sense. Amazing.
12. If chapter 3 would be scrapped and the introduction placed at the end, the book would certainly have a bit more of a David Lynch feeling.
13. If you picked up this book, you probably liked the front-cover. Lets hope you like the back-cover as well because the content is worthless.
14. The HERO died !!! Hopefully this is the last in the series.
15. Carefully consider other books before buying this miserable heap of recycled paper.
16. Hopefully the hero stays dead this time.
17. I loved the little troll on page 603.
18. The footnotes really deepened the story.
19. The book has a beginning, a middle and an end.
Obviously I’m highly frustrated with scientific reviewers 🙂
Managing Intelligent People
Two bulletpoints lists. The first taken via http://www.acceleratingfuture.com/michael/works/intelligentfailure.htm. The second from book. The first deals with the reason why intelligent people fail. The second deals with the management of such people.
Why Intelligent People Fail
Content from Sternberg, R. (1994). In search of the human mind. New York: Harcourt Brace.
1. Lack of motivation. A talent is irrelevant if a person is not motivated to use it. Motivation may be external (for example, social approval) or internal (satisfaction from a job well-done, for instance). External sources tend to be transient, while internal sources tend to produce more consistent performance.
2. Lack of impulse control. Habitual impulsiveness gets in the way of optimal performance. Some people do not bring their full intellectual resources to bear on a problem but go with the first solution that pops into their heads.
3. Lack of perserverance and perseveration. Some people give up too easily, while others are unable to stop even when the quest will clearly be fruitless.
4. Using the wrong abilities. People may not be using the right abilities for the tasks in which they are engaged.
5. Inability to translate thought into action. Some people seem buried in thought. They have good ideas but rarely seem able to do anything about them.
6. Lack of product orientation. Some people seem more concerned about the process than the result of activity.
7. Inability to complete tasks. For some people nothing ever draws to a close. Perhaps it’s fear of what they would do next or fear of becoming hopelessly enmeshed in detail.
8. Failure to initiate. Still others are unwilling or unable to initiate a project. It may be indecision or fear of commitment.
9. Fear of failure. People may not reach peak performance because they avoid the really important challenges in life.
10. Procrastination. Some people are unable to act without pressure. They may also look for little things to do in order to put off the big ones.
11. Misattribution of blame. Some people always blame themselves for even the slightest mishap. Some always blame others.
12. Excessive self-pity. Some people spend more time feeling sorry for themselves than expending the effort necessary to overcome the problem.
13. Excessive dependency. Some people expect others to do for them what they ought to be doing themselves.
14. Wallowing in personal difficulties. Some people let their personal difficulties interfere grossly with their work. During the course of life, one can expect some real joys and some real sorrows. Maintaining a proper perspective is often difficult.
15. Distractibility and lack of concentration. Even some very intelligent people have very short attention spans.
16. Spreading oneself too think or too thick. Undertaking too many activities may result in none being completed on time. Undertaking too few can also result in missed opportunities and reduced levels of accomplishment.
17. Inability to delay gratification. Some people reward themselves and are rewarded by others for finishing small tasks, while avoiding bigger tasks that would earn them larger rewards.
18. Inability to see the forest for the trees. Some people become obsessed with details and are either unwilling or unable to see or deal with the larger picture in the projects they undertake.
19. Lack of balance between critical, analytical thinking and creative, synthetic thinking. It is important for people to learn what kind of thinking is expected of them in each situation.
20. Too little or too much self-confidence. Lack of self-confidence can gnaw away at a person’s ability to get things done and become a self-fulfilling prophecy. Conversely, individuals with too much self-confidence may not know when to admit they are wrong or in need of self-improvement.
Zen and the Art of Research Management
John Naughton (Open University, Milton Keynes, England) , Robert W. Taylor (Woodside, California, USA)
1. Hire only the very best people, even if they are cussed. Perhaps especially if they are cussed. Your guiding principle should be to employ people who are smarter than you. One superb researcher is worth dozens of merely good ones.
2. Once you’ve got them, trust them. Do not attempt to micro-manage talented people. Set broad goals and leave them to it. Concentrate your own efforts on strategy and nurturing the environment.
3. Protect your researchers from external interference, whether from company personnel officers, senior executives or security personnel. Your job is to create a supportive and protective space within which they can work.
4. Much of what you will do will fall into the category of absorbing the uncertainty of your researchers.
5. Remember that you are a conductor, not a soloist. The lab is your performance.
6. Do not pay too much attention to ‘relevance’, ‘deliverables’ and other concepts beloved of Senior Management.
7. Remember that creative people are like hearts – they go where they are appreciated. They can be inspired or led, but not managed.
8. Keep the organization chart shallow. Never let the lab grow beyond the point where you cannot fit everyone comfortably in the same room.
9. Make your researchers debate with one another regularly. Let them tear one another’s ideas to pieces. Ensure frank communication among them. Observe the strengths and weaknesses which emerge in the process.
10. Be nice to graduate students. One day they may keep you, even if only as a mascot.
11. Install a world-class coffee machine and provide plenty of free soft drinks.
12. Buy descent chairs. Remember that most computer science research is done sitting down.
13. Institute a ‘toy-budget’, enabling anyone in the lab to buy anything costing less than a specified amount on their own authority. And provide a darkened recovery room for accountants shocked by the discovery of this budget.
14. Pay attention to what goes on in universities. Every significant breakthrough in computing in the last four decades has involved both the university and corporate sectors at some point in its evolution.
15. Remember to initiate and sponsor celebrations when merited.